
Preparing for a Joint Commission survey can be stressful, and there’s a lot of information to unpack. We want you to feel confident about your language access program whenever the big day arrives.
That’s why we went through the Joint Commission’s 800+ page manual to find and expand on language access standards. We’ve broken everything down into 6 simplified steps to help prepare your facility or health system comply with the Joint Commission standards.
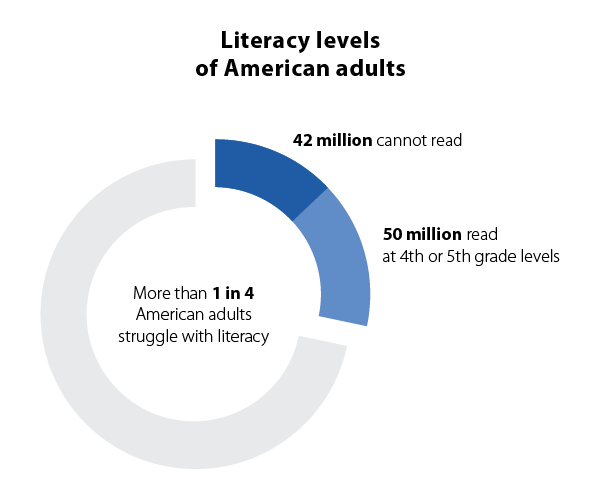
Your community’s diversity will help you decide what kind of language services and communication support your facility needs.
Standard
RI.01.01.03 The hospital respects the patient’s right to receive information in a manner the patient understands.
Elements of Performance (EP) 2. The hospital provides language interpreting and translation services. Note: The hospital determines which translated documents and languages are needed based on its patient population.
There are many demographic data sources for race, ethnicity, language, sexual orientation, and disability to help you determine who makes up your local community.
For the most accurate picture, look at data within the last 3 to 5 years.
You can also conduct focus groups or interview community leaders to identify demographic changes and community needs.
Fulfill two requirements at once – research the top 15 languages
Standard
RI.01.01.03
EP 1. The hospital provides information in a manner tailored to the patient’s age, language, and ability to understand.
STANDARD
RI.01.01.03
EP 2. The hospital provides language interpreting and translation services.
Note: Language interpreting options may include hospital-employed language interpreters, contract-interpreting services, or trained bilingual staff. These options may be provided in person or via telephone or video.
Interpretation – converting spoken and sign languages into other spoken languages
The Joint Commission leaves how to provide language services up to your organization. Which modes you use may depend on your budget and your hospital’s needs. You may want to create a list of language interpretation options and then develop supportive reasons to discuss with your decision-makers.
Options include:
Your plan may include a mixture of language services to cover 24 hours a day, seven days a week, and for various circumstances.
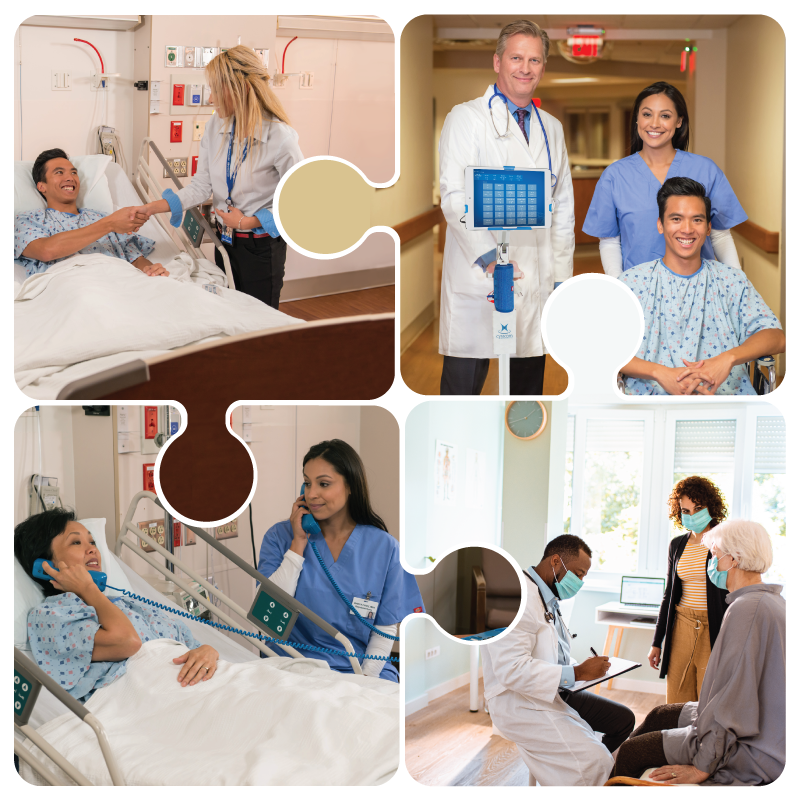

Translation – converting written text from one language into the written text of another language.
Determine which documents need to be translated into which languages to meet the needs of your patient population.
This could include vital and non-vital materials such as:
Finally, incorporate language services information into new or existing hospital policies and procedures—you can provide these documents to the Joint Commission when they come to your facility.
STANDARD
RI.01.01.03
EP 3. The hospital provides information to the patient who has vision, speech, hearing, or cognitive impairments in a manner that meets the patient’s needs.

![]()
![]()
Fulfill three requirements at once – providing means of communication for patients protected under the Americans with Disabilities Act and Section 1557 of the ACA.
If you decide to utilize trained bilingual staff for interpretation, make sure you follow the standard regarding defining and verifying their qualifications.
STANDARD
HR.01.01.01
The hospital defines and verifies staff qualifications.
EP 1. The hospital defines staff qualifications specific to their job responsibilities.
Note 4: Qualifications for language interpreters and translators may be met through language proficiency assessment, education, training, and experience. The use of qualified interpreters and translators is supported by the Americans with Disabilities Act, Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, and Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964.
If your staff is comfortable either communicating with their patients in their second language or working as an interpreter for other providers on an as-needed basis, make sure to assess their proficiency and then include this role in their official job descriptions. If you cannot assess language proficiency in-house, many external vendors can perform language proficiency assessments for you.
When hiring in-house language interpreters and translators, qualifications can consist of a language proficiency assessment, education, training, or experience. For sign language interpreters, consider requiring Registry of Interpreters for the Deaf (RID) certifications or an equivalent.
Fulfill two requirements at once – Section 1557 of the ACA also requires bilingual staff to have interpreting listed as part of their job description and be “qualified.”

Staff should feel comfortable accessing language services and working with interpreters.
Training should include:
We recommend making an eLearning training module or other official training documentation to present to the Joint Commission if they request it.
When hiring in-house language interpreters and translators, qualifications can consist of a language proficiency assessment, education, training, or experience. For sign language interpreters, consider requiring Registry of Interpreters for the Deaf (RID) certifications or an equivalent.
STANDARD
RC.02.01.01 The medical record contains information that reflects the patient’s care, treatment, and services.
EP 1. The medical record contains the following demographic information:
EP 25. The medical record contains the patient’s race and ethnicity.
If your hospital doesn’t currently address language preference, add new fill-in spaces, fields, or drop-down menus to initial admission patient forms to capture language data. The American Hospital Association Institute for Diversity and Health Equity (AHA IFDHE) has an excellent online resource, the Health Research and Educational Trust Disparities Toolkit, which goes into the details of collecting data.
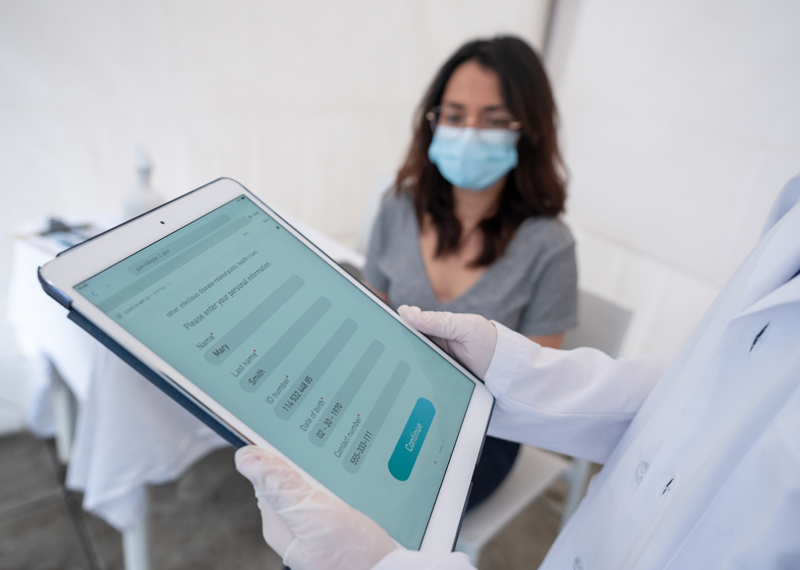


You can also create a process to help your staff identify patients with unique needs faster. For example:
Collecting patient language information may help you refine your results from Step 1. It could give you a clearer picture of your patient population, which your facility could use to develop or modify services, programs, or initiatives.
STANDARD
RI.01.01.01
The hospital respects, protects and promotes patient rights.
EP 1. The hospital has written policies on patient rights.
EP 2. The hospital informs the patient of the patient’s rights.
EP 5. The hospital respects the patient’s right to and need for effective communication.
EP 6. The hospital respects the patient’s cultural and personal values, beliefs, and preferences.
EP 9. The hospital accommodates the patient’s right to religious and other spiritual services.
EP 29. The hospital prohibits discrimination based on age, race, ethnicity, religion, culture, language, physical or mental disability, socioeconomic status, sex, sexual orientation, and gender identity or expression.
Several patient rights address the unique needs of individuals, such as the right to:
Fulfill two requirements at once – Section 1557 of the ACA also requires notices of nondiscrimination and taglines to be posted.
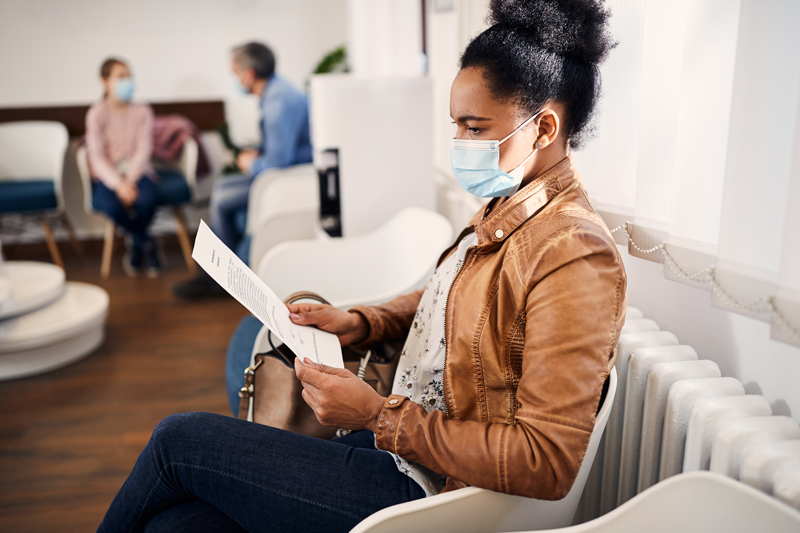
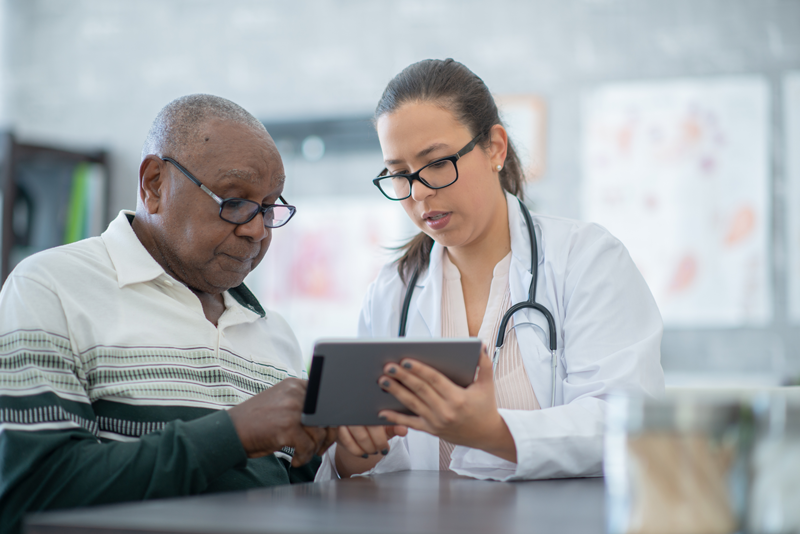
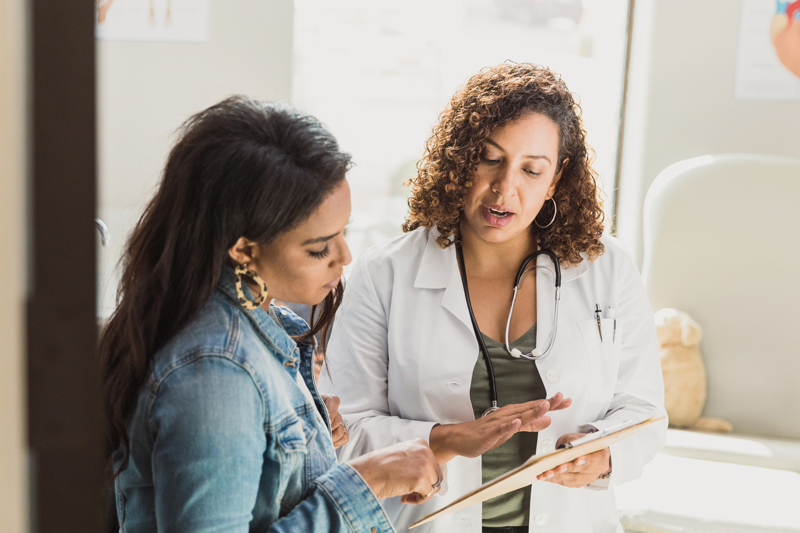




STANDARD
PC.02.01.21
The hospital effectively communicates with patients when providing care, treatment, and services.
EP 2. The hospital communicates with the patient during the provision of care, treatment, and services in a manner that meets the patient’s oral and written communication needs.

STANDARD
RI.01.03.01
The hospital honors the patient’s right to give or withhold informed consent.
EP 13. Informed consent is obtained in accordance with the hospital’s policy and processes and, except in emergencies, prior to surgery.

The informed consent process establishes a mutual understanding between patients and providers about the care, treatment, and services the patient will receive. For LEP patients, use translated informed consent materials in the patient’s language whenever possible. Even if your hospital provides translated materials, an interpreter during informed consent discussions can help facilitate thorough and transparent communication.
Staff should note the receipt of informed consent and any communication assistance used to obtain it in the medical record.

Have more questions?

For educational and informational purposes only. Not intended for legal use.
About CyraCom
In business for over 30 years, CyraCom is a language services leader that provides interpretation and translation services to thousands of organizations across the US and worldwide.
Sales Inquiries
New Client Signup &
Current Client Support
CyraCom Careers
Corporate Office
2650 E Elvira Rd, Suite 132
Tucson, AZ 85756
Sign in to your account